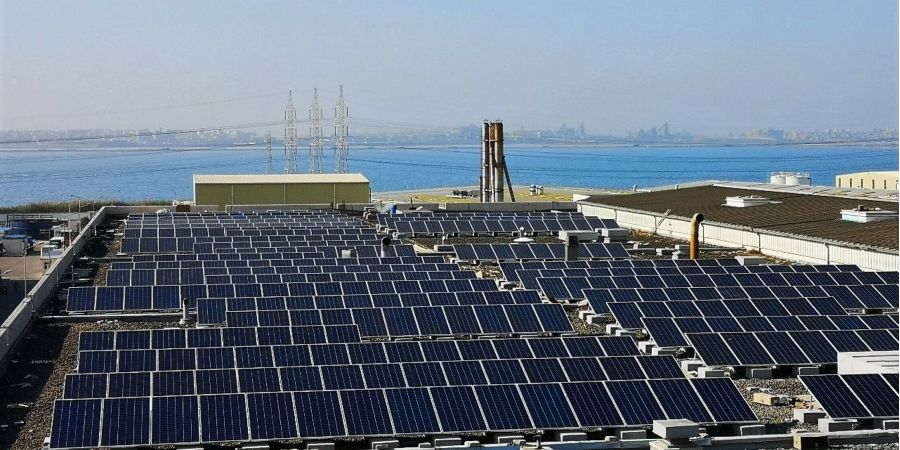
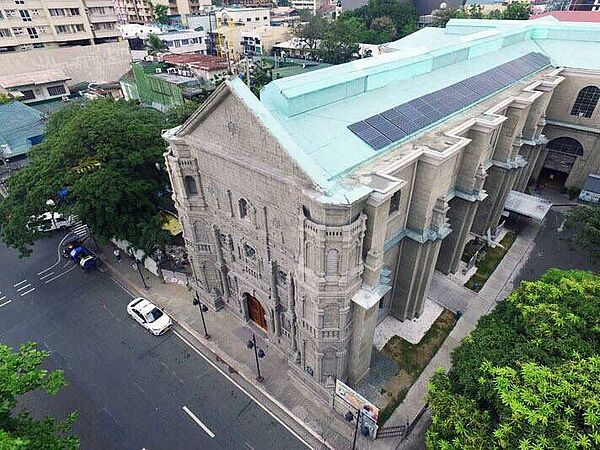
Background: The Government of Egypt is committed to increasing the share of renewables in the electricity mix to 42% by 2035. The country’s Nationally Determined Contribution (NDC) has led to the adoption of enabling measures to this end, including schemes to attract public and private investments under the Renewable Energy Law. Yet, contrary to over 1,500 MW utility-scale projects, grid-connected small-scale (rooftop, distributed) solar photovoltaics (PV) have not experienced the anticipated growth. There are around 63,000 industrial small and medium enterprise (SME) establishments in Egypt and conservative estimates of PV potential in the industrial sector exceed 1,000 MW (1 GW), yet PV deployment in industrial SMEs is significantly below market potential. With national installed capacity of ~60GW, and industry consuming around 27% of national electric energy from the carbon-intensive national grid (which accounts for 12% of national GHG emissions), stakeholders, experts, and market studies agree that solar PV for industrial SMEs have the potential to be unlocked via tailored measures.
The main barriers for a sector-wide transformation are (1) limited financial attractiveness and high perceived risk of investment and financing of PV in industrial SMEs; (2) weak project pipeline leadership; (3) limited & costly decision support for potential beneficiaries and financiers (4): weak monitoring systems and stakeholder engagement and (5) the perceived complexity of regulatory arrangements.
Approach to Transformational Change: “Egypt – Accelerating Deployment of Solar Energy in Industrial SMEs” or “Egypt – Solar PV Industry” for short, aims to unlock the potential in the industrial SME sector by removing the underlying barriers mentioned above and operationalising an enabling framework that allows solar PV business models to become financially self-sustainable. More specifically, the project’s objective is to support transformation to market-driven widescale deployment of on-grid solar PV in industrial SMEs through the installation of an exemplary 125 MW PV. Co-benefits of the project include cost reduction and increased competitiveness of industrial SMEs, local manufacturing promotion, green job creation, and air quality improvement. The project intends to demonstrate that public and private finance is leveraged, innovative financial solutions are viable, and enabling frameworks are in place for enhancing.
The financial component (FC) of the project consists of (1) a loan facility from own resources of two public commercial banks (2) grant co-finance of loan facility (3) equity from own resources of SMEs; and (4) partial grants to SMEs as investment incentive from Mitigation Action Facility funds. The project intends to leverage EUR 44 million of public co-funding.
Mitigation potential: The project is expected to directly result in at least 192,000 tCO2e avoided during the project and 1.5 million tCO2e avoided over technology lifetime.