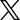Theory of Change
When launched in 2012, the Mitigation Action Facility, formerly known as the NAMA Facility, was instrumental in establishing the concept of ‘transformational change’. The concept has gained further momentum with the operationalisation of the Green Climate Fund (GCF) and is equally applied in the Paris Agreement. The Mitigation Action Facility continues its focus on catalysing transformational change towards sustainable carbon-neutral development, supporting the Paris Agreement’s objective to limit the increase in global average temperature ‘to well below 2 °C above pre-industrial levels and to pursue efforts to limit the temperature increase to 1.5 °C above pre-industrial levels’.
The Mitigation Action Facility emphasises how a mix of different types of interventions – in particular, regulatory and financial ones – may trigger behaviour, consumption and production methods in developing countries that are conducive to carbon-neutral development. Mitigation Action Facility support enables public and private actors in developing countries and emerging economies to address financial barriers to behaviour change, consumption and production patterns, and the use of carbon-neutral technologies. The project portfolio demonstrates that across the various sectors, carbon-neutral technologies can become economically viable and thus encourage and facilitate further investments in broader mitigation measures within a sector.
The Theory of Change (ToC) seeks to illustrate the transformational potential by depicting the pathway of changes that shall be initiated through the Mitigation Action Facility support. These desired changes are primarily triggered by the individual projects. Projects shall demonstrate how climate finance will effectively contribute to a transformational change. Given the Mitigation Action Facility’s objective of supporting implementation of ambitious mitigation measures to drive decarbonisation in priority sectors, the focus of projects is on financial support mechanisms that serve to mobilise capital investments in and operation of carbon-neutral alternatives. Technical support and institutional and regulatory capacity development in partner countries may be provided during project implementation to facilitate this objective. The underlying assumptions behind the ToC can be found in the supporting narrative document. The ToC is divided into impact, outcome, outputs, activities and inputs, as shown below:
Impact
Transition towards carbon-neutral societies to keep temperature rises below 1.5 degrees C is supported by projects in the partner countries
Increased mitigation ambition
Financing of sector-wide mitigation improved
National capacities strengthened
Behavioural change catalysed
Outcome
The Mitigation Action Facility demonstrates that climate finance can effectively catalyse transformational change in countries – including implementation of Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) – reduce greenhouse gas emissions and enhance carbon-neutral development
Outputs
Output 1
The Mitigation Action Facility is effective and efficient in catalysing transformational mitigation action to implement NDCs and LTS
Output 2
Additional public and private finance is supported to drive carbon-neutral development
Output 3
The Mitigation Action Facility disseminates lessons from transformational mitigation action, contributing to an effective learning environment
Output 4
National and local stakeholders have enhanced their capacities and policy environment to implement transformational mitigation actions
Output 5
Implemented projects produce sustainable and transformative co-benefits
Activities
Programme activities
– Pipeline development and steering
– Coordination and engagement with the Mitigation Action Facility Board
– Support and guidance to projects
– Fostering strategic partnerships
Cross-cutting activities
– Learning-oriented M&E
– Documentation, transfer and uptake of knowledge amongst projects
– Communication of lessons learnt
– Facilitation of learning, replication, and exchange with other programmes
Project activities
Implementation activities in the priority sector, such as:
– Piloting innovative financing models to overcome market barriers to carbon-neutral development
– Deploying innovative technologies and approaches
– Developing national capacities
– Engaging with the public and private sectors
– Cooperating with similar projects
Inputs
TSU
Mitigation Action Facility funding: Germany, UK, EU, Denmark, CIFF
Projects
Other projects in the country / sector
NDCs
National policies & long-term strategies